Diabetes Complications Wiki
Type 2 Diabetes Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). From wikipedia, the free encyclopedia diabetes mellitus type 2 (or adult-onset diabetes) is a metabolic disorder diabetes complications wiki where high levels of blood sugar occur. left untreated, it can cause heart attacks, strokes, blindness and kidney failure. Younger people have more years with diabetes ahead, so their goal may be lower to reduce the risk of complications, unless they often have hypoglycemia (low blood sugar, or a “low”). people who are older, have severe lows, or have other serious health problems may have a higher goal.
Diabetes Wikipedia
Introducing pietro marsala diabetes complications wiki @marsala90, diabetes warrior, and now, eligible commercial pilot. read more about how the ada advocated for this change, here (link in story): bit. ly/2rnfdab or visit diabetes. org for more connectedforlife. Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). if you. Targets vary with the type of diabetes, age, and presence of complications. if you have gestational diabetes, your blood sugar targets will be lower than people with other types of diabetes.
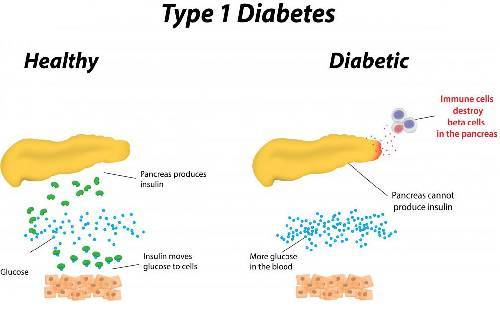
Aims: the diabetes complications severity index (dcsi) converts diagnostic codes and laboratory results into a 14-level metric quantifying the long-term effects of diabetes on seven body systems. adoption of the international classification of diseases, tenth revision, clinical modification (icd-10-cm) necessitates translation from icd-9-cm and. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. type 1 diabetes mellitus happens when the part of the pancreas that makes insulin is destroyed by that person’s own immune system. when the pancreas does not make insulin, glucose sugar in the blood cannot get into the parts of the body that need sugar to live. In almost all high-income countries, diabetes is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation. maintaining blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol at or close to normal can help delay or prevent diabetes complications. therefore people with diabetes need regular monitoring.
International Diabetes Federation Complications
Complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes: the person will need insulin and possibly blood pressure and other medications, depending on any complications they have. type 2 diabetes: some people will need to use diabetes complications wiki insulin, or. Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or.
Diabetic retinopathy eyewiki.
Diabetes complications. if it is not controlled, diabetes can cause a host of complications that can affect nearly every organ in the body. diabetes complications include: heart disease. stroke. Possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary nerve damage (neuropathy). excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish your kidney damage. The primary complications of diabetes due to damage in small blood vessels include damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. damage to the eyes, known as diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina of the eye, and can result in gradual vision loss and eventual blindness. [34].
Early, correct diagnosis and symptom management is the best way to avoid complications from type 1. 5 diabetes. written by kathryn watson on november 2, 2018. related stories. Although long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually, they can eventually be disabling or even life-threatening. some of the potential complications of diabetes include: heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis). Diabetes type 1 and type 2 facts. diabetes is a chronic condition associated with abnormally high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. insulin produced by the pancreas lowers blood glucose. absence or insufficient production of insulin, or an inability of the body to properly use insulin causes diabetes. the two types of diabetes are referred to as type 1 and type 2. Diabetes type 2 is the most common form of diabetes mellitus in the world. insulin resistance by the body is the regularly observed cause of diabetes type 2. however, there is also another uncommon factor which causes diabetes type 2, that is, the body simply does not produce enough insulin.
Complications. poorly managed diabetes can lead to heart attacks, strokes, blindness and kidney failure. treatment. type 2 diabetes can often be treated just by losing weight and exercising more, as these increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin. a medicine called metformin is often prescribed, which works by helping the fat and muscle. The diabetes control and complications trial (dcct) demonstrated that strict glycemic control targeting lower hba1c goals among patients with t1dm can both delay the onset of retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy and slow the progression of existing microvascular complications. The diabetes control and complications trial (dcct) demonstrated that strict glycemic control targeting lower hba1c goals among patients with t1dm can both delay the onset of retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy and slow the progression of existing microvascular complications. this came at the expense of a threefold higher risk of. Complications of hypertension are clinical outcomes that result from persistent elevation of blood pressure. hypertension is a risk factor for all clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis since it is a risk factor for atherosclerosis itself. it is an independent predisposing factor for heart failure, coronary artery disease, stroke, kidney disease, and peripheral arterial disease.
Immune compromise respiratory infections such as pneumonia and influenza are more common among individuals with diabetes. lung function is increased risk of wound infections restrictive lung disease is known to be associated with diabetes. lung restriction in diabetes could result diabetes complications wiki from chronic Diabetes is a condition that results from lack of the hormone insulin in a person's blood, or when the body has a problem using the insulin it produces (insulin resistance). there is another disease with a similar name, diabetes insipidus, however they are not related. when people say "diabetes", they usually mean diabetes mellitus. people with diabetes mellitus are called "diabetics". Some of the potential complications of diabetes include: heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure nerve damage (neuropathy). excess sugar can cause tingling, numbness, burning or pain that usually begins at the tips.

Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of consciousness. a person's breath may develop a specific "fruity" smell. onset of symptoms is usually rapid. Diabetes control and complications trial research group. clustering of long-term complications in families with diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial. diabetes. 1997 nov; 46:1829-39. diabetic retinopathy clinical research network. a randomized trial comparing intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide and focal/grid. The complications of diabetes mellitus are far less common and less severe in people who have well-controlled blood sugar levels. acute complications include hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, diabetic coma, and nonketotic hyperosmolar coma. chronic complications occur due to a mix of microangiopathy, macrovascular disease and immune dysfunction in the form of autoimmune disease or poor immune. Microvascular complications damage to both tiny and large blood vessels due to uncontrolled blood glucose which may lead to eye, kidney or nerve diseases. macrovascular complications plaque build up in the in the arteries leading to possible heart attack or stroke. what is the treatment for diabetes type 1? medical treatment.
Comments
Post a Comment