Diabetes Mellitus Complication
If the glucose levels become very high, you may develop a condition called gestational diabetes mellitus (gdm). the condition is so named because it first begins or is discovered during pregnancy. Nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). about half of all people with diabetes have some form of nerve damage. read more. foot complications. diabetes mellitus complication learn about neuropathy (which can cause numbness in the feet) as well as other complications. read more. dka (ketoacidosis) & ketones.
Diabetesmellitus is a prolonged health condition that needs persistent attention to prevent acute complications. research has shown that millions of people are infected with diabetes globally.
Periodontal Disease The Sixth Complication Of Diabetes Mellitus
Up to 50% of people with diabetes are thought to have a mental illness such as depression or anxiety. diabetes more than doubles the risk of depression. people with diabetes and depression may have increased risk of other complications from diabetes, as they may find it harder to manage everyday tasks, and their diabetes may become neglected. In people with diabetes macrovascular complications are two times greater than microvascular complications 20% 9% 0 5 10 15 20 25 macrovascular complications microvascular complications in 9 ) adapted from turner r et al ann intern med 1996;124:136-145. The complications of diabetes mellitus can be divided into acute and chronic categories. acute complications primarily include diabetic ketoacidosis (discussed later in this chapter), nonketotic hyperosmolar syndrome, and hypoglycemia.
Complications Of Diabetes Guide To Diabetes Diabetes Uk
See more videos for diabetes mellitus complication. Based on etiology, diabetes is classified as type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 diabetes mellitus, latent autoimmune diabetes, maturity-onset diabetes of youth, and miscellaneous causes. the.
Diabetes Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Other complications of diabetes mellitus. this photo shows an erythematous papule with a central yellow plaque on the leg of a patient with necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum. necrobiosis lipoidica is characteristic but not diagnostic of diabetes. lesions most often appear on the legs and begin as erythematous papules that develop into atrophic. Diabetesmellitus is a disease often called sugar diabetes because the condition makes it difficult to convert food to energy. long-term complications can affect many parts of your body. The acute complications of diabetes may also happen when insulin therapy is suddenly withdrawn, or when infection, surgery or other stressful events occur. the two acute complications of diabetes mellitus are diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar non-ketotic diabetic coma.

Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus Endocrine And Metabolic

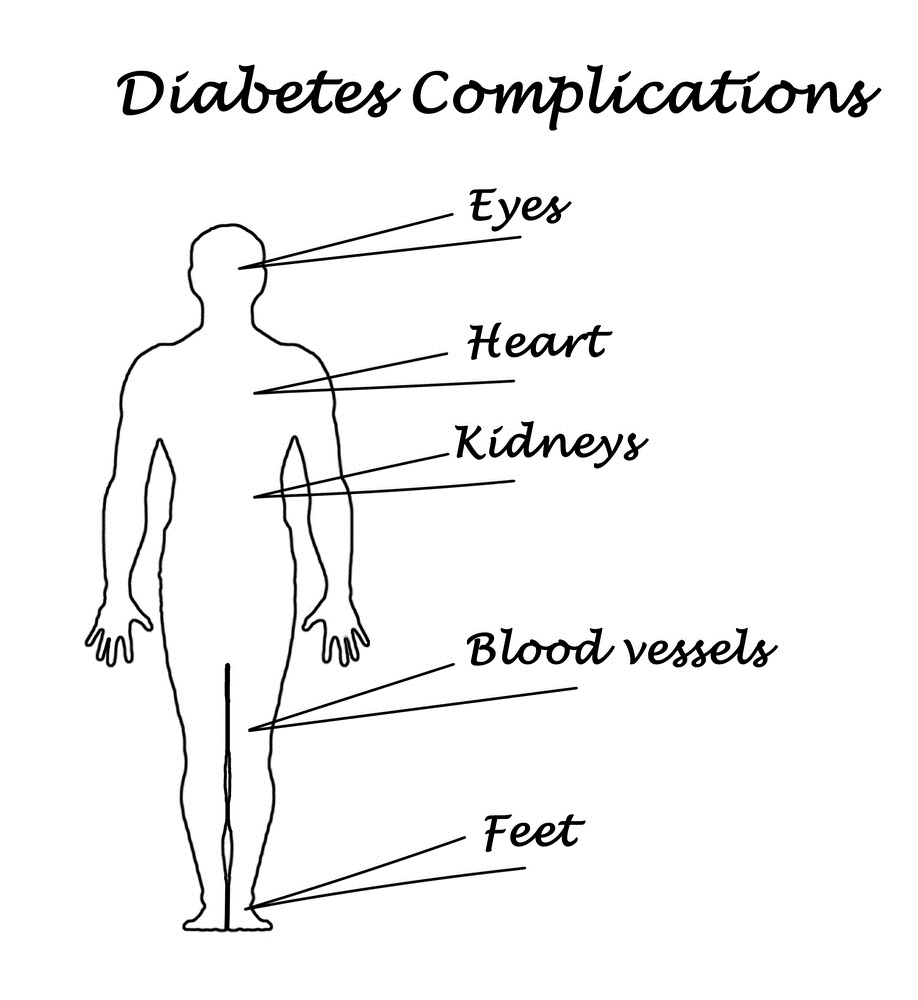
Uncontrolled diabetes means your blood sugar levels are too high, even if you're treating it. and you may have symptoms such as peeing more often, being thirsty a lot, and having other problems. Diabetesmellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. diabetes mellitus complication nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee).
Skin complications. diabetes can affect every part of the body, including the skin. in fact, such problems are sometimes the first sign that a person has diabetes. luckily, most skin conditions can be prevented or easily treated if caught early. some of these problems are skin conditions anyone can have, but people with diabetes get more easily. Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by destruction of the periodontal tissues and resulting in loss of connective tissue attachment, loss of alveolar bone, and the formation of pathological pockets around the diseased teeth. some level of periodontal disease has been found in most populations studied and is responsible for a substantial portion of the tooth. Some women with diabetes may have irregular periods and may have problems getting pregnant. diabetes increases the risk for dementia. diabetes increases the risk of bone diseases, including osteoporosis. low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) from treatment of diabetes can also increase the risk of heart disease. Complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels.
However, because type 2 diabetes may be present for some time before it is diagnosed, complications in type 2 diabetes may be more serious or more advanced when they are discovered. people with diabetes mellitus may experience many serious, long-term complications. In patients with diabetes mellitus (dm), years of poorly controlled hyperglycemia lead diabetes mellitus complication to multiple, primarily vascular, complications that affect small vessels (microvascular), large vessels (macrovascular), or both. the mechanisms by which vascular disease develops include. Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. the longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. A complication of diabetes mellitus that is frequently overlooked or under-reported is cognitive decline, which was first reported almost a century ago and can occur with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. 46–49 an elevated risk of dementia, cerebral atrophy, and presence of white matter abnormalities have been shown in multiple studies.
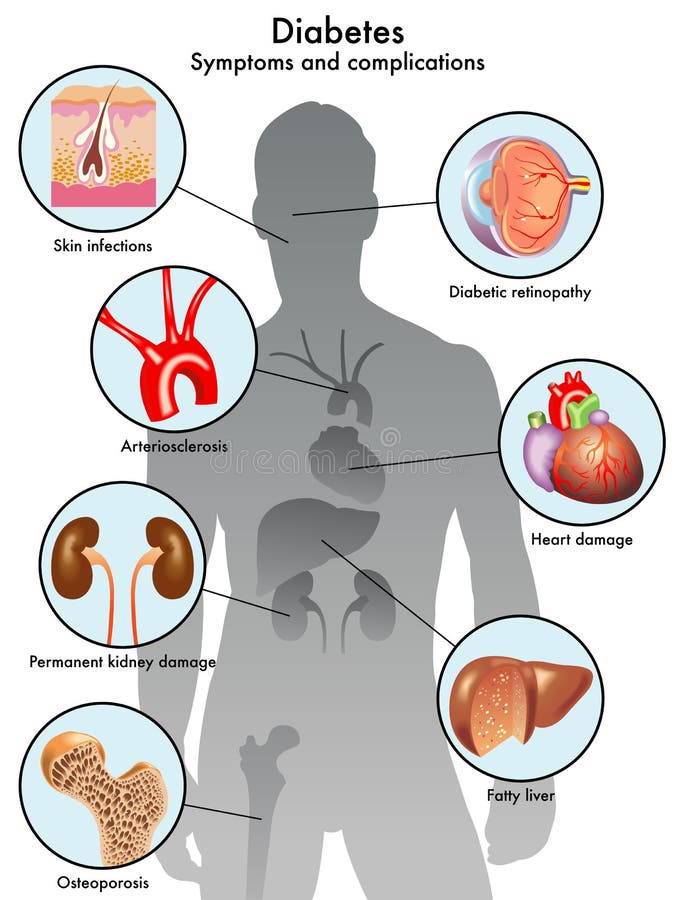
But the most important ways to slow diabetes complications are to keep your blood sugar levels under control, eat right, exercise, lose weight, avoid smoking, and get high blood pressure and high. Cardiovascular disease: affects the heart and blood vessels and may cause fatal complications such as coronary artery disease (leading to heart attack) and stroke. cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in people with diabetes. high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high blood glucose and other risk factors contribute to increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary nerve damage (neuropathy). excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish your kidney damage. The culprit in fungal infections of people with diabetes is often candida albicans. this yeast-like fungus can create itchy rashes of moist, red areas surrounded by tiny blisters and scales. these infections often occur in warm, moist folds of the skin.
What is type 2 diabetes mellitus? type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease. it is characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood. type 2 diabetes is also called type 2 diabetes mellitus and adult-onset diabetes. that's because it used to start almost always in middleand late-adulthood. Diabetes is a group of chronic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia. modern medical care uses a vast array of lifestyle and pharmaceutical interventions aimed at preventing and controlling hyperglycemia. in addition to ensuring the adequate delivery of glucose to the tissues of the body, treatment of diabetes attempts to decrease the likelihood that the tissues of the body are harmed by. Although long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually, they can eventually be disabling or even life-threatening. some of the potential complications of diabetes include: heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis).
Comments
Post a Comment