Diabetes Obesity And Metabolism
The institute for diabetes, obesity and metabolism at the university of minnesota is uniquely poised to become a premier research institute that is focused on advancing knowledge of the pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications through cutting edge research. It is my privilege to serve as director of the ua center for disparities in diabetes, obesity and metabolism. the center will serve as a nucleus for interdisciplinary research that forms the foundation for translation of biomedical research to advanced, evidence-based clinical care in the community in order to facilitate the development of innovative approaches diabetes obesity and metabolism to delivery of care and. The journal impact 2019-2020 of diabetes, obesity and metabolism is 6. 560, which is just updated in 2020. compared with historical journal impact data, the factor 2019 of diabetes, obesity and metabolism dropped by 9. 02 %. the journal impact quartile of diabetes, obesity and metabolism is q1. the journal impact of an academic journal is a scientometric factor that reflects the yearly average.
The mission of the institute for diabetes, obesity and metabolism is to support and develop successful approaches to the prevention, treatment, and cure of diabetes mellitus and obesity. the leadership of the idom embraces a disease-oriented approach that focuses on type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular complications. Metabolism and obesity. according to the center for disease control (2015-2016 data) the prevalence of obesity is 39. 6% for us adults. diabetes obesity and metabolism the health care costs associated with obesity are estimated at over $147 billion annually due to associated chronic metabolic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer. Diabetes, obesity and metabolism is primarily a journal of clinical and experimental pharmacology and therapeutics covering the interrelated areas of diabetes, obesity and metabolism.
Mechanism Linking Diabetes Mellitus And Obesity
Mechanism linking diabetes mellitus and obesity.
Diabetes Obesity And Metabolism 201920
Welcome To The Institute For Diabetes Obesity And Metabolism
Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews. accepted articles. review article. free access. obesity and diabetes as high‐risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (covid ‐19). The journal impact 2019 of diabetes, obesity and metabolism is 6. 560, which is just updated in 2020. the journal impact measures the average number of citations received in a particular year (2019) by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years (2017-2018). Diabetes & metabolism publishes high-quality original research papers by internationally leading teams, forming a close link between hospital and research units. official publication of the french society for the study of diabetes (sfd), the journal features original articles, short reports and comprehensive reviews. Researchers within the diabetes, obesity and metabolism research focus area have expertise in studying bile acid, glucose, lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. yanqiao zhang, m. d. director dr. zhang’s group focuses on understanding how bile acid, lipid or glucose homeostasis is maintained under normal and disease conditions.
Journalguide Diabetes Obesity And Metabolism
The seminar series at the center on diabetes, obesity and metabolism (cdom) is intended to provide the wake forest community with exposure to cutting-edge developments in the broad field of metabolism. the audience includes clinical and basic investigators in fields that range from population sciences to molecular biology. Introduction. diabetes mellitus (dm) is a chronic disorder that can alter carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. it is caused by the absence of insulin secretion due to either the progressive or marked inability of the β-langerhans islet cells of the pancreas to produce insulin, or due to defects in insulin uptake in the peripheral tissue. Circulating branched-chain amino acids (bcaas) associate with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. 3-hydroxyisobutyrate (3-hib) is a catabolic intermediate of the bcaa valine. here we show that in a cohort of 4,942 men diabetes obesity and metabolism and women, circulating 3-hib is elevated according to levels of hyperglycemia and established type 2 diabetes. in complementary cohorts with measures of insulin resistance.
3hydroxyisobutyrate A Strong Marker Of Insulin

The institute for diabetes, obesity and metabolism was established in 2005 by the dean of the school of medicine, at a time of ever increasing prevalence of diabetes and obesity. in the united states alone, there are currently 20. 6 million people with diabetes and 58 million obese. Diabetes obesity & metabolism impact factor, if, number of article, detailed information and journal factor. issn: 1462-8902. See more videos for diabetes obesity and metabolism.
Launched in 2020, dom now complements the prestigious journal diabetes, obesity & metabolism (dom), by curating newsworthy and highly-valued enhanced content for busy healthcare professionals. click here to find out more. Diabetes, obesity and metabolism is primarily a journal of clinical and experimental pharmacology and therapeutics covering the interrelated areas of diabetes, obesity and metabolism. the diabetes obesity and metabolism journal prioritises high-quality original research that reports on the effects of new or existing therapies, including dietary, exercise and lifestyle (non-pharmacological) interventions, in any aspect of metabolic and endocrine disease, either in humans or animal and cellular systems. Launched in 2020, dom now complements the prestigious journal diabetes, obesity & metabolism (dom), by curating newsworthy and highly-valued enhanced content for busy healthcare professionals. click here to find out more.
Description. this journal aims to provide a forum for publication of clinical and experimental pharmacology studies related to diabetes, obesity and metabolism, including evaluations of new glucose and weight-lowering drugs, new therapeutic developments in the management and prevention of diabetic complications, e. g. growth factors and biotechnology products for foot ulcers, and clinical. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism is primarily a journal of clinical and experimental pharmacology and therapeutics covering the interrelated areas of diabetes, obesity and metabolism. the journal prioritises high-quality original research that reports on the effects of new or existing therapies, including dietary, exercise and lifestyle (non. Endnote styles diabetes, obesity and metabolism. all clarivate analytics websites use cookies to improve your online experience.
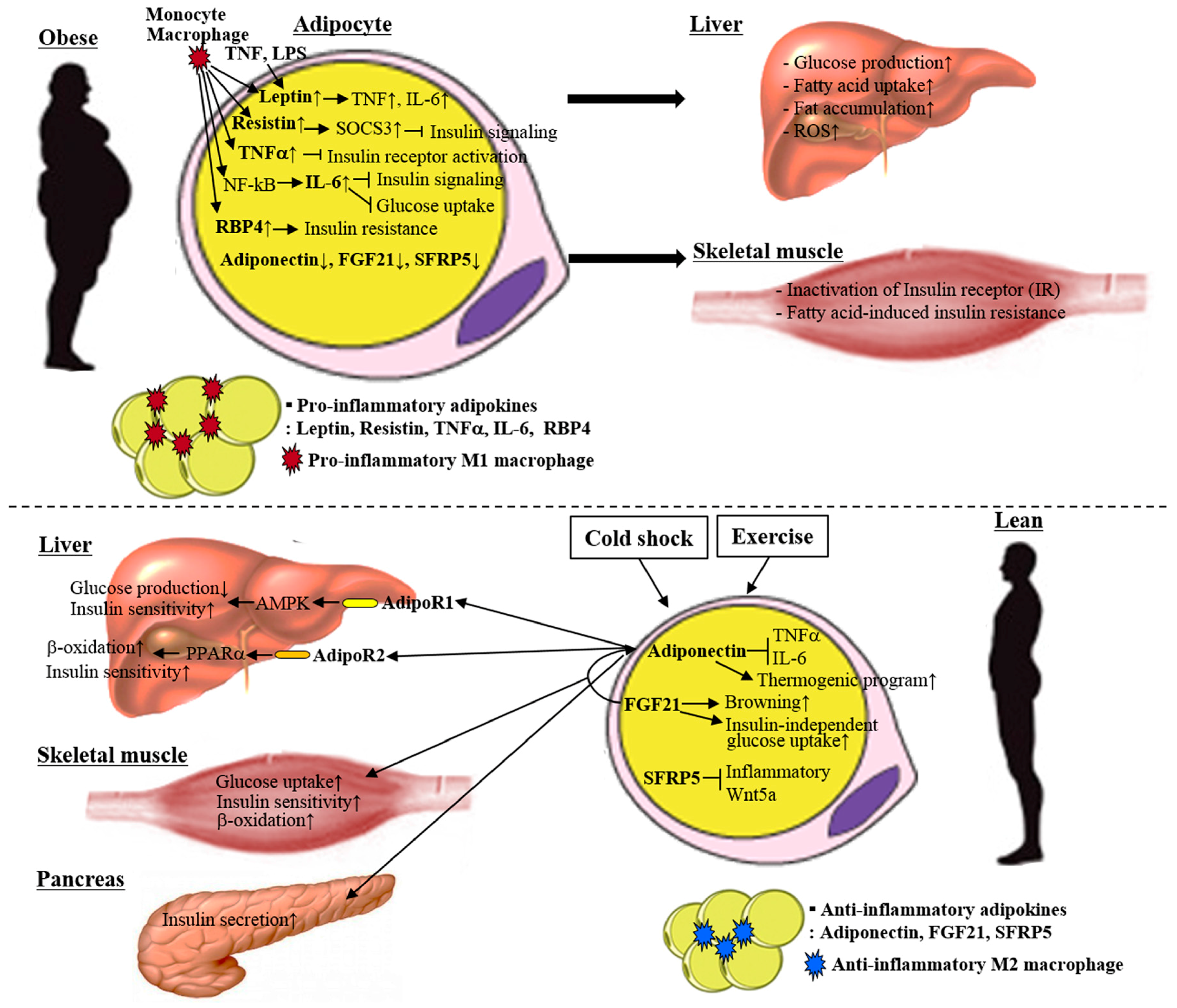
Authors are reminded that diabetes, obesity and metabolism is primarily a journal of pharmacology and therapeutics. the scope of the journal includes human pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, cost-effectiveness studies, preclinical pharmacology, and phase i-iv clinical trials. Chapter 6 role of mitochondria in the skeletal muscle metabolism in obesity and type 2 diabetes. paula m. miotto and graham p. holloway. pages 155-172. abstract. skeletal muscle, by virtue of its mass and high rate of metabolism, represents an important tissue in the context of impaired glucose homeostasis. although the underlying mechanism(s. Diabetes, obesity and metabolism: a journal of pharmacology and therapeutics is the only interdisciplinary journal for high-quality research and reviews in the areas of diabetes, obesity and metabolism. it focuses on clinical and experimental pharmacology diabetes obesity and metabolism and therapeutics in any aspect of metabolic and endocrine disease, either in humans or animal and cellular systems. Diabetes and obesity are chronic disorders that are on the rise worldwide. body mass index has a strong relationship to diabetes and insulin resistance. in an obese individual, the amount of nefa, glycerol, hormones, cytokines, proinflammatory substances, and other substances that are involved in the development of insulin resistance are increased.
Comments
Post a Comment