Cdc Diabetes Mortality
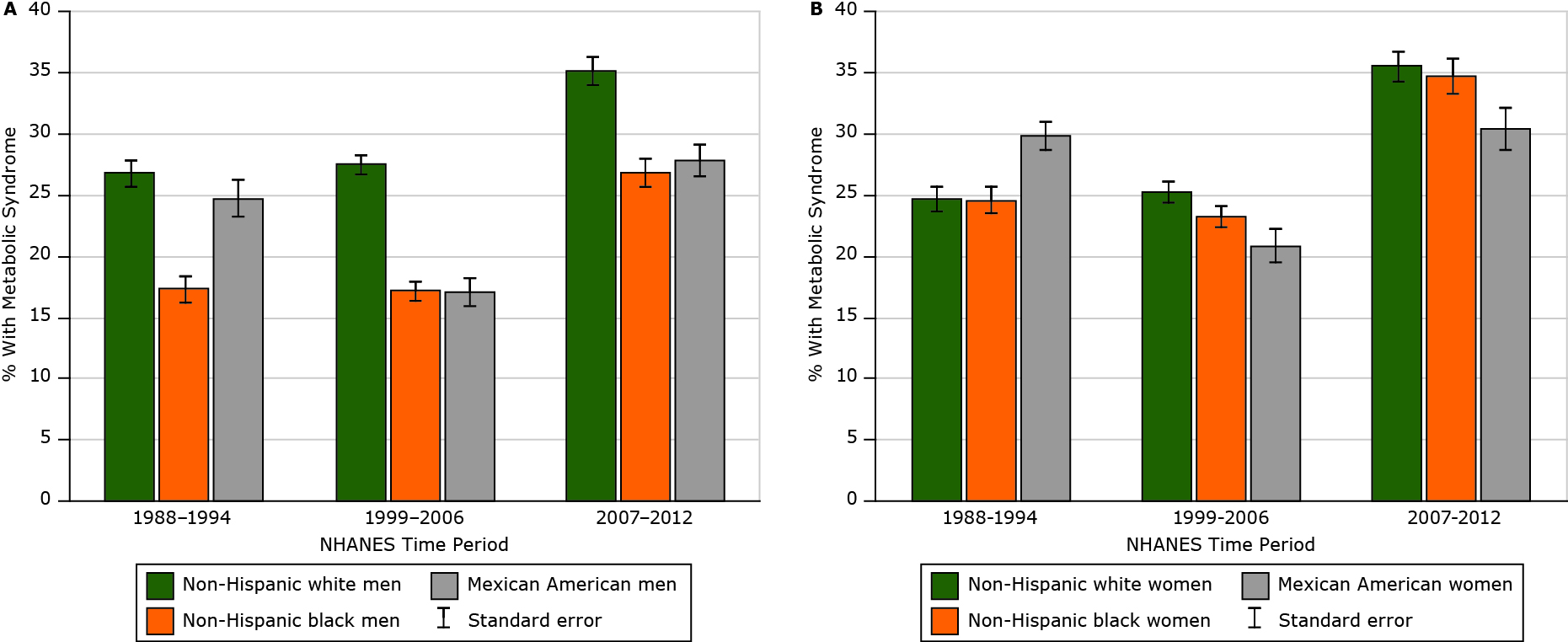
About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. it develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults (but more and more in children, teens, and young adults). you may not notice any symptoms, so it’s important to get your blood sugar tested if you’re at risk. Men with diabetes had larger decreases in cvd death than women with diabetes (p < 0. 001). conclusions: major cvd mortality in adults with diabetes has declined, especially in men. large reductions were observed for ihd and stroke mortality, although heart failure and cdc diabetes mortality arrhythmia deaths did not change.
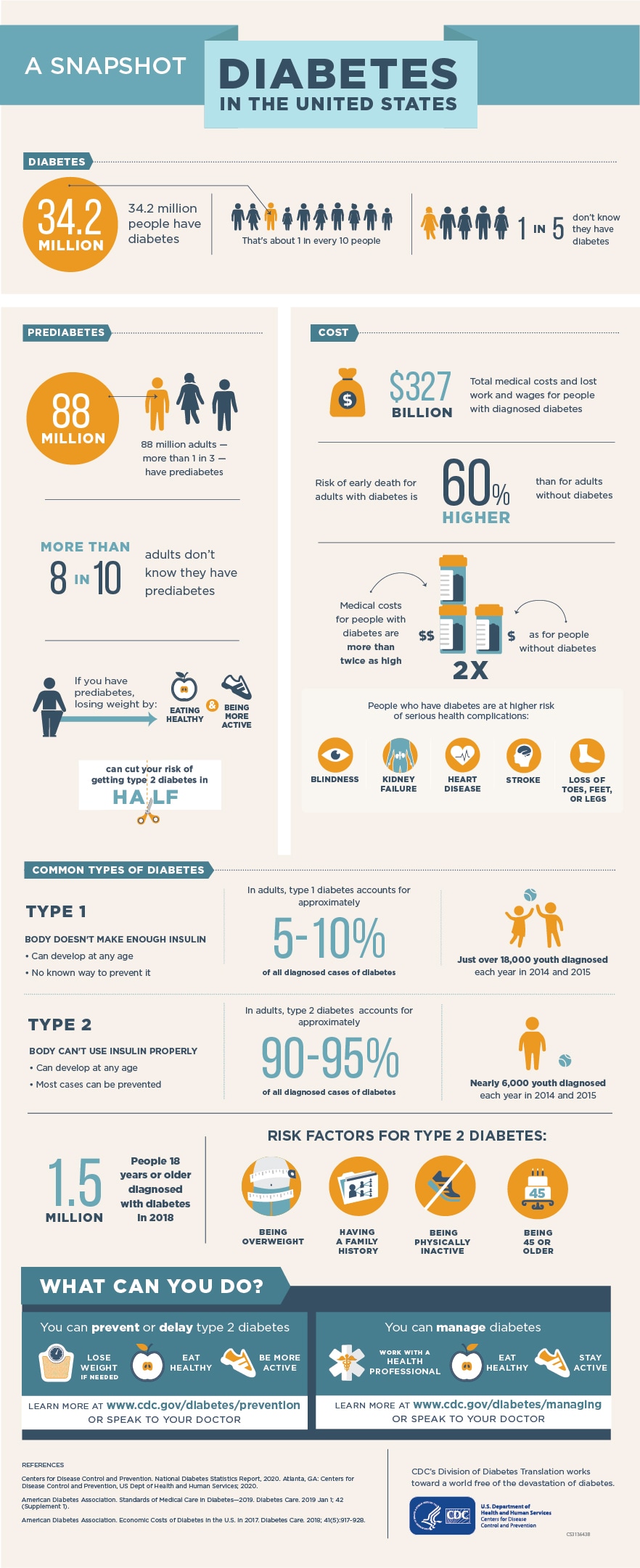
Cdc says diabetes, lung disease, heart disease and smoking may increase risk of severe coronavirus illness published tue, mar 31 2020 5:11 pm edt updated tue, mar 31 2020 6:05 pm edt berkeley. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the united states. diabetes is the no. 1 cause of kidney failure, lower-limb amputations, and adult blindness. in the last 20 years the number of adults diagnosed with diabetes has more than doubled. Diabetes, including type 1, type 2, or gestational, may put people at higher risk of severe illness from covid-19. actions to take. continue taking your diabetes pills and insulin as usual. test your blood sugar every four hours and keep track of the results. make sure that you have at least a two-week supply of your diabetes pills and insulin. Diabetes is one of the most prevalent and serious chronic diseases in the united states. more than 30 million (9. 4%) people in the united states have diabetes, and 1 in 4 of them don’t know they have it (source: cdc national diabetes statistics report, 2017). in 2015, approximately 1. 5 million new cases of diabetes were diagnosed in adults ages 18 years and older, and that number is.
Data sources: centers for disease control and prevention, national center for health statistics. multiple cause of death 1999-2013 from cdc wonder online database. the number of deaths with diabetes as ucd corresponds to death certificate reports where diabetes was ascertained to be the disease that initiated the chain of morbid events that led. Cdcdiabetes state burden toolkit. estimated quality adjusted life years (qalys), united states, 2013 quality-adjusted life years (qalys) is a measure that combines quality of life (qol) and life expectancy. qol is measured on a scale from 0 to 1, where 0 represents death and 1 represents perfect health. Multiple cause of death 1999-2013 from cdc wonder online database. the number of deaths with diabetes as ucd corresponds to death certificate reports where diabetes was ascertained to be the disease that initiated the chain of morbid events that led directly and inevitably to death.
Diabetesmortality. this section of the burden toolkit reports estimated diabetes mortality statistics in your state for people aged 15 years or older. this data consists of the number of deaths, rate of deaths per 100,000 people, years of life lost, and quality-adjusted life years. While there is no proven direct connection between diabetes and death from covid-19, the journal of the american medical association (jama) reports on a higher case-fatality rate among those with. Access the diabetes atlas, a web app that allows you to view diabetes surveillance data at national, state, and county levels. morbidity and mortality weekly report; diabetes state burden toolkit. page last reviewed: may 30, the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. For more information, please call 1-800-diabetes (800-342-2383) our friends at sansum diabetes research institute (sdri) have created a website and helpline for the hispanic/latino population. for bilingual resources, visit latinodiabetes. sansum. org or call (805) 350-8730.
Mortality Burden Toolkit Centers For Disease Control
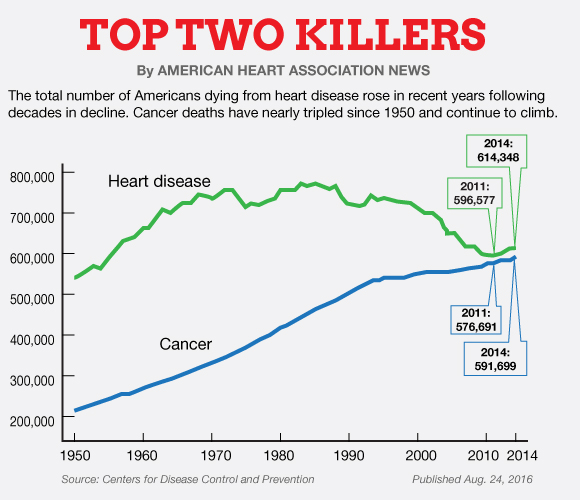
The national diabetes statistics report pdf icon [pdf 768 kb] is a periodic publication of the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the united states for a scientific audience.. the report includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications. Number of deaths for leading causes of death: heart disease: 647,457 cancer: 599,108 accidents (unintentional injuries): 169,936 chronic lower respiratory diseases: 160,201 stroke (cerebrovascular diseases): 146,383 alzheimer’s disease: 121,404 diabetes: 83,564 influenza and pneumonia: 55,672. Diabetes and african americans. african american adults are 60 percent more likely than non-hispanic white adults to have been diagnosed with diabetes by a physician. in 2016, cdc diabetes mortality non-hispanic blacks were 3. 5 times more likely to be diagnosed with end stage renal disease as compared to non-hispanic whites.
Diabetes Cause Of Death Burden Toolkit
Eye disorders and vision loss among u. s. adults aged 45 and over with diagnosed diabetes, 2016–2017. prevalence of total, diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes among adults: united states, 2013 2016. emergency department visits by patients aged 45 and over with diabetes: united states, 2015. Mortality. this section of the burden toolkit reports estimated diabetes mortality statistics in your state for people aged 15 years or older. this data consists of the number of deaths, rate of deaths per 100,000 people, years of life lost, and quality-adjusted life years. to view your state's statistics on diabetes mortality, click on the appropriate item on the left hand side of the screen.
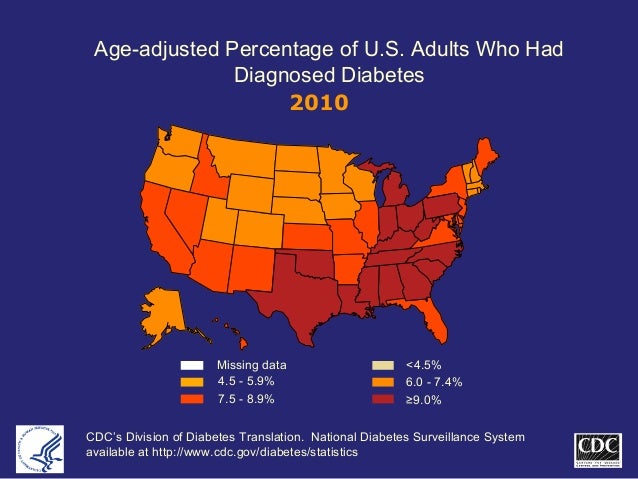
Source: wonder. cdc. gov states are categorized from highest rate to lowest rate. although adjusted for differences in age-distribution and population size, rankings by state do not take into account other state specific population characteristics that may affect the level of mortality. Cdcdiabetes state burden toolkit. incidence of diagnosed diabetes in adults, aged 18-76 years old, united states, 2013. The number of diabetes-attributable deaths is reported in two ways. one section of data reports the number of deaths with diabetes as the underlying cause of death. the other section reports the number of diabetes-attributable deaths with all causes of death and underlying causes of death, which could have been cardiovascular disease or end-stage renal disease.
Diabetes Data And Statistics Cdc
Diabetes mortality by state. related pages. 1 the number of deaths per 100,000 total population. source: wonder. cdc. gov. states are categorized from highest rate to lowest rate. although adjusted for differences in age-distribution and population size, rankings by state do not take into account other state specific cdc diabetes mortality population.
What is diabetes? cdc.
Mortality number of diabetes-attributable deaths. the number of diabetes-attributable deaths is reported in two ways. one section of data reports the number of deaths with diabetes as the underlying cause of death. the other section reports the number of diabetes-attributable deaths with all causes of death and underlying causes of death, which. Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the cdc website.. the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by cdc or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website. Number of deaths: 2,813,503; death rate: 863. 8 deaths per 100,000 population; life expectancy: 78. 6 years; infant mortality rate: 5. 79 deaths per 1,000 live births.
Comments
Post a Comment